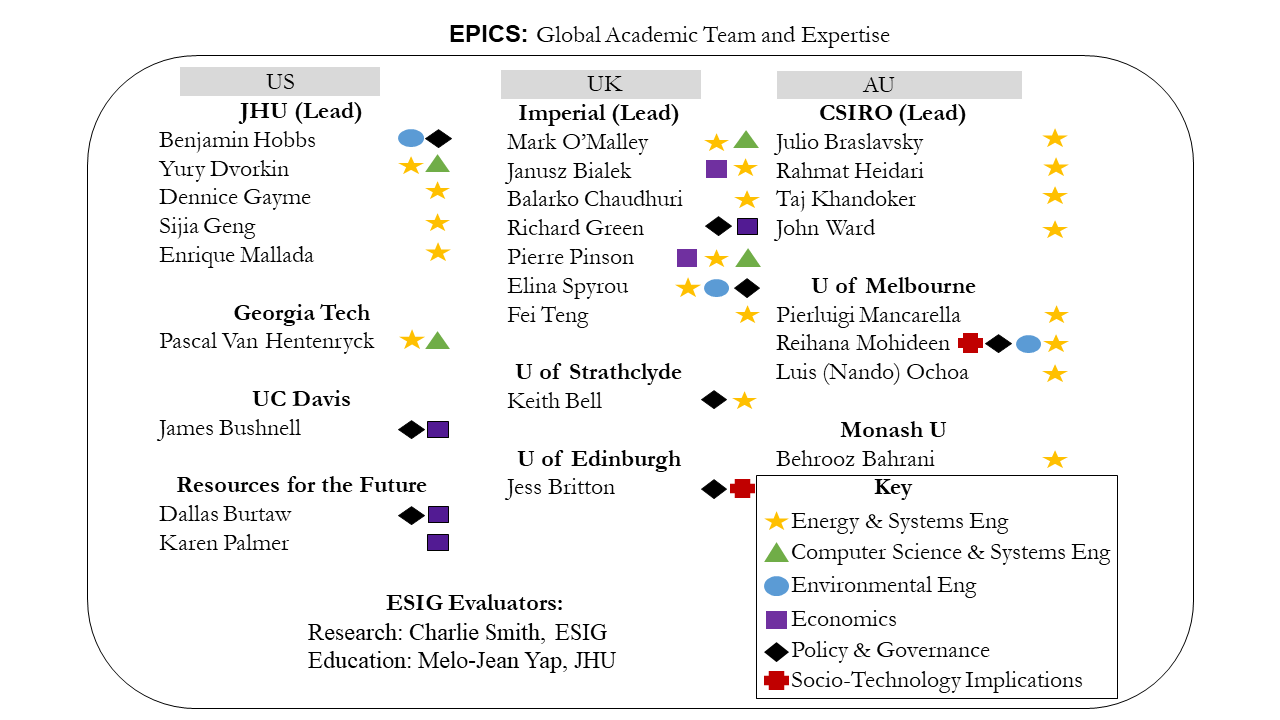
The Electric Power Innovation for a Carbon-free Society (EPICS) Center is an NSF Global Center for use-inspired research addressing global challenges in climate change and clean energy that is led by Johns Hopkins University (JHU) and based out of the Ralph O’Connor Sustainable Energy Institute (ROSEI). EPICS in the UK and Australia are funded by the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) and are led by Imperial College London and University of Melbourne. Georgia Tech, University of California-Davis, University of Strathclyde, University of Edinburgh, Monash University, and Resources for the Future are also collaborators.
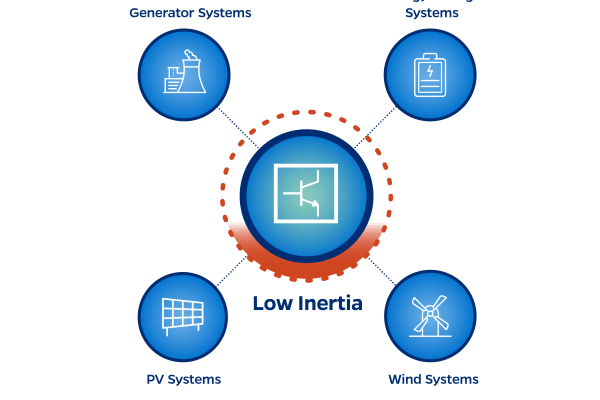
The transition from traditional electric power grids, powered mainly by large fossil-fuel generators, to clean-power power grids with wind, solar, and batteries, necessitates overhauling power system economics, operation and control, with crucial emphasis on inverters demanding the development of new services, tools, and methods for effective system functioning and studies.
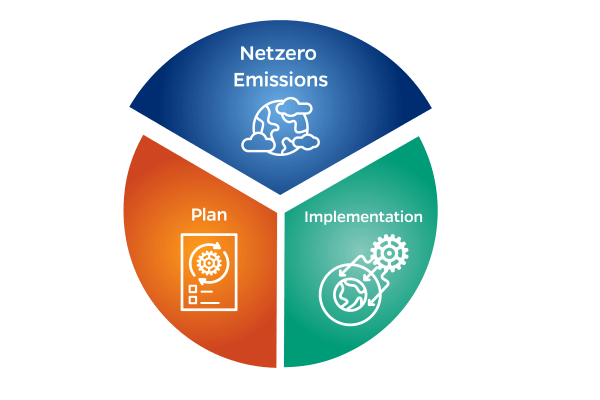
EPICS will develop computing, economic, engineering, and policy methods and tools to enable a 100% emissions-free power grid. The center’s research interests are divided into four thrusts, which will:
- Harness the latest advances in computer technology to enable decision-making tools to handle the unpredictable nature of renewable energy resources like wind and solar.
- Find ways to accommodate wind, solar and storage resources into the grid, which requires learning how to operate large numbers of inverters that connect these resources and the grid.
- Develop economic analysis principles tailored for making decisions about how to design and then reliably operate 100% renewable power grids.
- Use insights from the above efforts to develop strategies for achieving net-zero power grids globally, and use them to reduce and eventually eliminate carbon emissions from other economic sectors, including transportation and buildings.
Through collaboration with global partners, this agenda will produce material changes to today’s power system management and institutions (e.g., electricity markets, policy, and regulation) that allow for harvesting the full potential of inverter-based variable renewable energy resources (VRE), energy storage and distributed energy resources (DER) technologies without sacrificing efficiency, affordability, reliability, resiliency, and the pace of achieving climate pledges.